contact dermatitis guidelines (pdf) guidelines for the management of contact dermatitis: an update
Atopic eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, it can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to manage and alleviate the symptoms of atopic eczema. One valuable resource that provides guidelines for the treatment of atopic eczema is a publication titled “Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema.” These guidelines have been developed by a panel of experts in the field and aim to provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based recommendations to assist in the management of this condition. The guidelines emphasize the importance of a multi-faceted approach to treatment, including regular use of emollients, topical corticosteroids, and topical calcineurin inhibitors. Emollients play a fundamental role in hydrating the skin, reducing itchiness, and acting as a barrier against environmental triggers. They should be applied liberally and frequently to affected areas. In cases where the eczema flare-ups are more severe, the guidelines recommend the use of topical corticosteroids. These medications help to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms such as redness and itching. It is important to note that the strength of the corticosteroid should be matched to the severity of the symptoms, and they should be used for short periods to minimize potential side effects. For individuals who may not respond adequately to topical corticosteroids or have contraindications to their use, topical calcineurin inhibitors can be an alternative. These medications help to modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation without the side effects associated with corticosteroids. They are particularly useful for sensitive areas such as the face and neck. It is essential to emphasize the importance of regular moisturization and avoiding triggers that can exacerbate atopic eczema. Environmental factors, such as exposure to irritants, allergens, and extreme temperatures, can contribute to flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help to reduce the frequency and severity of eczema symptoms. In addition to topical treatments, other therapeutic options may be considered for individuals with moderate to severe atopic eczema. These include phototherapy, systemic immunosuppressants, and biologic therapies. Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light, which can help to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms. Systemic immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed in severe cases to modulate the immune response and control eczema flare-ups. Biologic therapies, which target specific molecules involved in the immune response, have shown promising results in clinical trials and may provide significant relief for some patients. It is crucial for individuals with atopic eczema to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan. Each person’s experience with atopic eczema is unique, and therefore treatment approaches may vary. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to assess the efficacy of the treatment plan and make any necessary adjustments. In conclusion, managing atopic eczema requires a comprehensive approach that includes a combination of topical treatments, moisturization, trigger avoidance, and potentially other therapeutic options for more severe cases. The “Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema” serve as a valuable resource for healthcare professionals in developing an evidence-based treatment plan. By following these guidelines and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with atopic eczema can find relief and improve their quality of life. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or adjusting any treatment for atopic eczema.
If you are searching about (PDF) Guidelines for the management of contact dermatitis: an update you’ve came to the right place. We have 5 Pictures about (PDF) Guidelines for the management of contact dermatitis: an update like Contact Dermatitis Nursing Care Management and Study Guide | Nursing, Contact Dermatitis Guidelines 2017 | Dermatitis | Allergy and also Contact Dermatitis Guidelines 2017 | Dermatitis | Allergy. Here you go:
(PDF) Guidelines For The Management Of Contact Dermatitis: An Update
 www.academia.eduLooking At Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Options | Contemporary Pediatrics
www.academia.eduLooking At Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Options | Contemporary Pediatrics
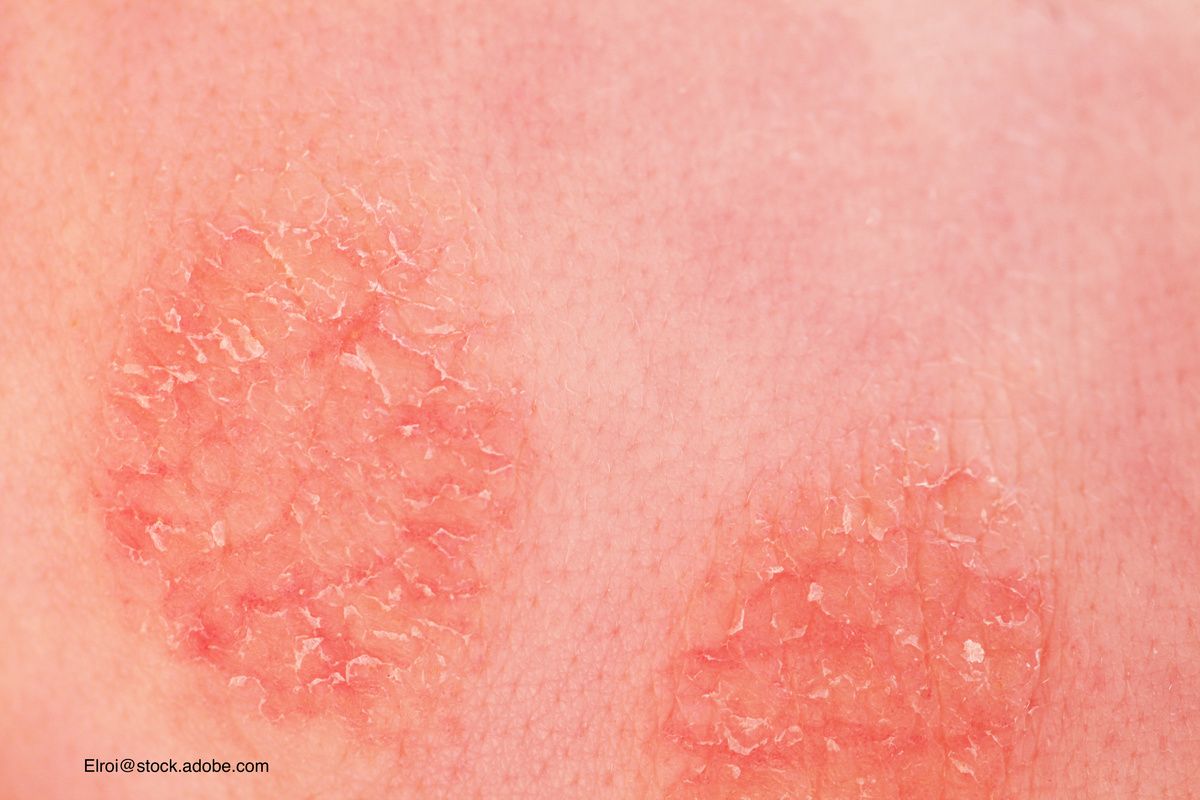 www.contemporarypediatrics.comdermatitis atopic treatment pediatrics
www.contemporarypediatrics.comdermatitis atopic treatment pediatrics
Contact Dermatitis Guidelines 2017 | Dermatitis | Allergy

Consensus‐based European Guidelines For Treatment Of Atopic Eczema
 www.onlinelibrary.wiley.comeuropean dermatitis atopic treatment guidelines eczema consensus part dermatology interdisciplinary adults based children venereology academy
www.onlinelibrary.wiley.comeuropean dermatitis atopic treatment guidelines eczema consensus part dermatology interdisciplinary adults based children venereology academy
Contact Dermatitis Nursing Care Management And Study Guide | Nursing
 www.pinterest.comnursing care dermatitis contact plan nurseslabs
www.pinterest.comnursing care dermatitis contact plan nurseslabs
Consensus‐based european guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema. Dermatitis atopic treatment pediatrics. Contact dermatitis nursing care management and study guide